Blog
Effects Of Drugs On Sports Performance

In the high-stakes arena of elite sports, the difference between a gold medal and historical obscurity is often measured in fractions of a second or millimeters of movement. While training, nutrition, and genetics lay the foundation, the pursuit of the “biological edge” has led to a complex relationship between pharmacology and physiology.
Performance-enhancing substances (PEDs) are often discussed in hushed tones of scandal, but scientifically, they represent a fascinating – albeit controversial – hacking of human biology. They do not create magic; rather, they hijack specific physiological pathways to accelerate recovery, amplify power, and extend endurance beyond natural ceilings.
This article dissects the physiological mechanisms of these substances, categorizing them by the biological systems they optimize.
Safety First: The analysis below is strictly educational. However, for those choosing to pursue performance enhancement, product quality is critical to safety. We strongly recommend that any performance-enhancing drugs or sports supplements be purchased exclusively from verified, reputable sources to avoid the dangers of underground contamination. For example, for high-quality performance enhancers and steroidal products, readers in Canada may verify established suppliers like Oxygen Anabolic. Always consult a medical professional before beginning any regimen.
1. Musculoskeletal Enhancement: The Power Engine
The Goal: Hypertrophy, maximum force production, and explosive power.
At the cellular level, muscle growth (hypertrophy) is a mathematical balance between protein synthesis (building) and proteolysis (breakdown). Anabolic agents, primarily testosterone derivatives and synthetic steroids, fundamentally alter this equation.
By binding to androgen receptors within the muscle cells, these agents signal the nucleus to increase the production of proteins, specifically actin and myosin – the contractile filaments that generate force. Simultaneously, they inhibit the effects of cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone which causes muscle breakdown.
The Result:
- Lean Mass Accrual: Athletes can build muscle mass at a rate that defies natural synthesis limits.
- Force Output: A larger muscular cross-section allows for greater contraction force, directly translating to speed in sprinters and power in lifters.
- Structural Integrity: Many agents also increase bone density, providing a skeletal frame capable of withstanding the increased torque of stronger muscles.
2. Cardiovascular & Metabolic Optimization: The Endurance Engine
The Goal: Oxygen delivery, fatigue delay, and energy efficiency.
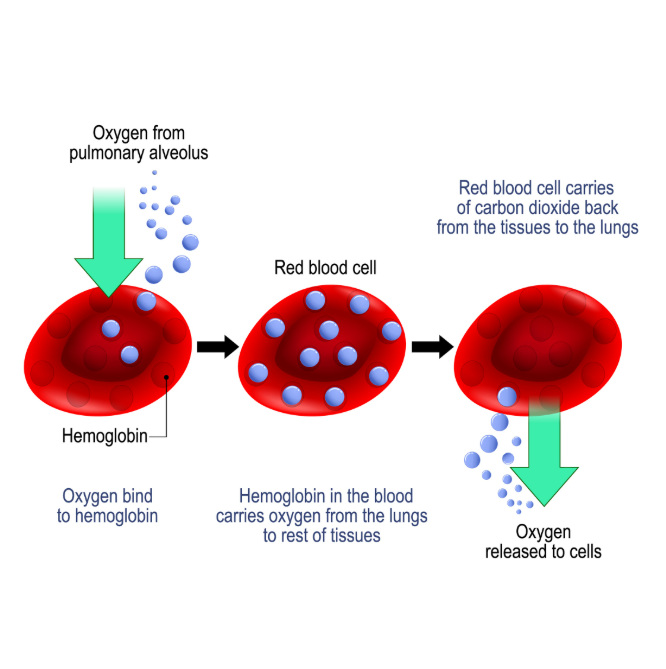
For endurance athletes like cyclists and marathon runners, the limiting factor is rarely muscle strength, but rather the supply of oxygen to the working tissue. This is defined by VO2max – the maximum rate of oxygen consumption.
Agents like Erythropoietin (EPO) target the bone marrow to stimulate hematopoiesis – the production of red blood cells. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, the protein vehicle that transports oxygen from the lungs to the muscles.
The Mechanism:
- Hematocrit Boost: By artificially raising the hematocrit (the percentage of blood volume made up of red blood cells), the blood’s oxygen-carrying capacity skyrockets.
- Metabolic Shifting: Certain metabolic modulators can also influence the mitochondria to burn fatty acids more efficiently than carbohydrates. This “glycogen sparing” effect ensures that the athlete’s premium fuel reserves (glycogen) last longer during grueling events, delaying the onset of “hitting the wall.”
3. Neurological & Cognitive Precision: The Control Center
The Goal: Focus, reaction time, and tremor reduction.
In sports, power is useless without control. The Central Nervous System (CNS) acts as the command center, and different disciplines require opposite chemical interventions.
Stimulants (The Accelerators):
Compounds like amphetamines work by increasing the synaptic concentration of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine.
- Effect: This heightens alertness, reduces the subjective perception of fatigue, and measurably decreases reaction time – critical for baseball batters or goalies.
Beta-Blockers (The Stabilizers):
Conversely, precision sports like archery, shooting, or biathlon require a decoupling of adrenaline and physical reaction. Beta-blockers bind to epinephrine receptors to mute the “fight or flight” response.
- Effect: This lowers the heart rate and, crucially, eliminates physiological tremors (shaking hands), allowing for robot-like steadiness during the release of a shot.
4. Accelerated Recovery: The Restoration System
The Goal: Repair velocity and training volume capacity.
Perhaps the most profound effect of performance enhancement is not what happens during the event, but what happens after. Natural physiology dictates a refractory period – time needed to repair micro-tears in muscle and connective tissue.
Substances like Human Growth Hormone (HGH) and specific peptide chains accelerate collagen synthesis. They act as a supercharged repair crew for tendons, ligaments, and muscle fibers.
The Edge:
The primary benefit here is training volume. An enhanced athlete can perform a high-intensity workout, recover completely within 12 hours, and repeat it. A natural athlete might require 48 to 72 hours for the same recovery. Over a four-year Olympic cycle, this accumulates into thousands of additional hours of high-quality training.
Conclusion
The effects of drugs on sports performance are not merely about “getting strong” or “going fast.” They represent a calculated manipulation of human physiology. By chemically optimizing the power engine, the endurance system, the control center, and the recovery cycle, these substances allow the human body to operate in a zone that biology never intended to unlock.